RUNLTS: Register-value-aware Predictor Utilizing Nested Large Tables 论文与源代码阅读笔记
对 CBP-6 冠军项目 RUNLTS 分支预测器论文和源代码的阅读笔记。
本文原为之前汇报所用,迁移至此,比较杂乱。
Block quote in this note is used to show the relevant part in the original code.
Overview
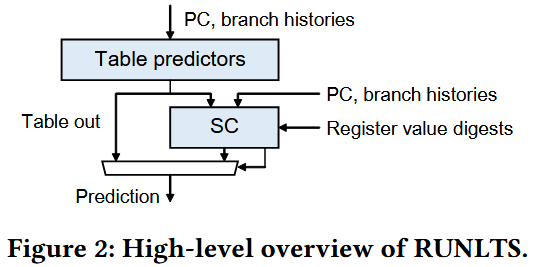
RUNLTS 全称是 Register-value-aware predictor Utilizing Nested Large TableS,论文、源代码、PPT 和演讲视频可以在 CBP2025 Workshop Program 中找到。
To exploit correlations with register values, we feed not only the PC and branch history but also register-value digests into the SC.
TAGE
Structure
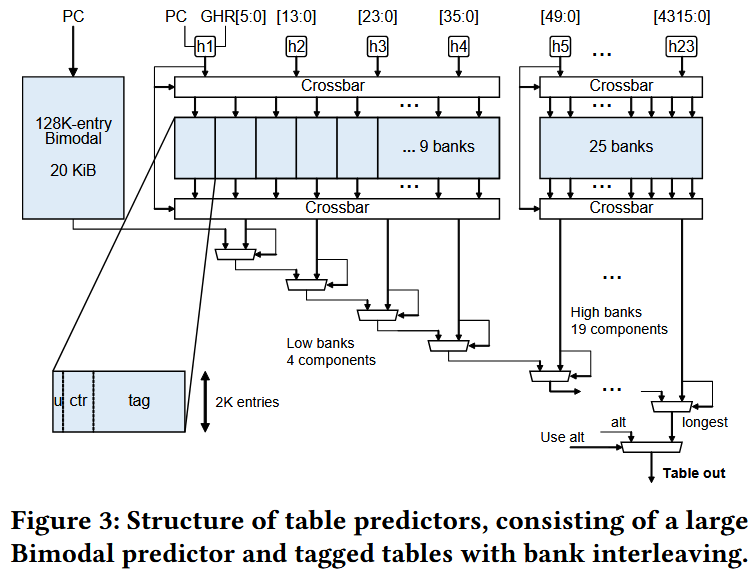
1 Bimodal and 23 Taggged Tables
Bimodal
indexed by PC
bim_pred: 128K ents. * 1 bit/ent. (1 for taken)
bim_hyst: 32K ents. * 1 bit/ent.
Bimodal hysteresis shared by 4 ents.
Tagged Tables
Structure
Entry
class gentry
useful_or_newly_alloc (1-bit)
The u-bit is set not according to whether its prediction was correct but according to whether the entry is deemed useful; it is set if omitting that entry would have caused a misprediction.
ctr (3-bit)
≥0 for taken
tag (9-bit for low banks, 13-bit for high banks)
Organization
init_histories
Low Banks: 4 components, 9 banks
High Banks: 19 components, 25 banks
2K ents./bank

How to access an entry: gtable[pv.HitBank][pv.GI[pv.HitBank]
HitBank: 1 ~ 23, the id of logical tables
Prepare_GI_GTAG_BI
GI contains the physical offset with consideration of bank id. (the actual offset relative to gtable[1] or gtable[5])
表内偏移由 PC、全局历史、路径历史 生成
逻辑表到bank的映射:根据 PC、路径历史 决定,相邻 bank round-robin 分配
Tag由 PC、全局历史、路径历史 生成
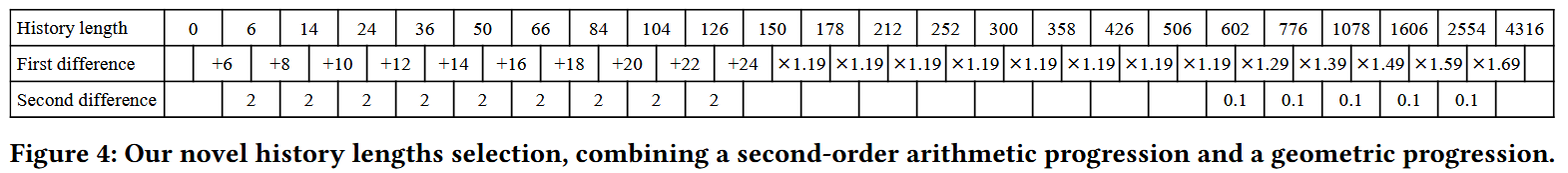
History Lengths
The method that combines a second-order arithmetic progression with a geometric progression (Figure 4) is near-optimal.
Predict
Tagepred
Look for the bank with longest matching history and the alternate bank, both default prediction is Bimodal.
use_alt_on_na: 16 ents. * 5 bits/ent.
indexed by HitBank and AltConf
在TAGE_allocation中训练:当最长匹配表ctr = 0 or -1,在LongestMatchPred != alttaken的情况下更新,如果alt正确则增,否则减
If the entry’s ctr = 0 or -1 and USE_ALT_ON_NA is ≥ 0, use the alternate prediction. Otherwise use LongestMatchPred.
这里
USE_ALT_ON_NA的 index 计算方法为((((pv.HitBank - 1) / 8) << 1) + pv.AltConf) % (SIZEUSEALT - 1),其中HitBank最大为 23,AltConf为 0 或 1,所以(((pv.HitBank - 1) / 8) << 1) + pv.AltConf)其实只会产生 0 ~ 5,并没有用到 16 个表项。事实上这个计算方法就是 Andre Seznec 在 CBP-5 所使用的。
Update
Tagged-Table Allocation
Combinations in which the prediction counter is 0 or −1 and the u-bit is set rarely appear.
Re-purpose these combinations as an explicit marker for newly allocated entries: when an entry is allocated, we initialize its counter to 0 or −1 and set the u-bit to 1, and we clear the u-bit as soon as the entry is referenced.
So storage-free.
two Allocation Monitoring Counters (16-bit each) tracking
NewlyDecay: the number of times they are evicted without being referenced.
NewlyUseful: the number of times these newly allocated entries lead to correct predictions.
Entry allocation rate is adjusted based on the ratio of successful predictions to evictions.
TAGE_allocation
TAGE预测错误且HitBank不是最长历史表(指 表23)时
如果ctr为0 or -1,且最长匹配表预测正确,不分配
如果预测器整体预测正确(即被SC纠正),有31/32的概率不分配
否则进行分配
TAGE_do_allocation
Allocation Throttling (idea from BATAGE):有用的新条目越多,分配越激进
ratio = NewlyDecay / NewlyUseful
控制(1)这次最多尝试多少次分配(2)遇见新分配条目是否替换
ratio <= 2: 4 (AggressiveAllocation)
2 < ratio <= 4: 3
4 < ratio: 2 (ModestAllocation)
从HitBank+1或+2开始
在AggressiveAllocation且条目为新分配的情况下,不进行替换,但清除useful_or_newly_alloc位
否则在新分配(ctr = 0 or -1)或 not useful(useful_or_newly_alloc = 0)的情况下,替换
如果not useful,但置信度还比较高,ctr向反方向变化
如果useful,则不替换,本次尝试分配失败,++NumberOfBlocks
将最后一次替换的条目useful_or_newly_alloc置位
TICK_update
U-bit monitoring counter: TICK (10-bit) TICK += (NumberOfBlocks - 2 * NumberOfAllocations);
利用NumberOfBlocks和NumberOfAllocations动态追踪有多少 entry 被视为“有用”,当“有用太多”时,就清除掉一些“use”位,防止资源被过度占用
清除u位策略:清除tagged tables中所有非新分配表项的useful_or_newly_alloc位
Train
TAGE_train
当HitBank为Tagged Tables时
当最长匹配预测失败且置信度很低,更新alt
当最长匹配预测正确且为新分配,++NewlyUseful
更新最长匹配
若最长匹配置信度太低,清除useful_or_newly_alloc
The second-longest-match entry has high confidence and provides the same direction and it’s correct, remove ‘useful’.
若没有Tagged Table匹配,更新Bimodal
若最长匹配与Alt相反且预测正确,置位useful_or_newly_alloc
SC
Structure
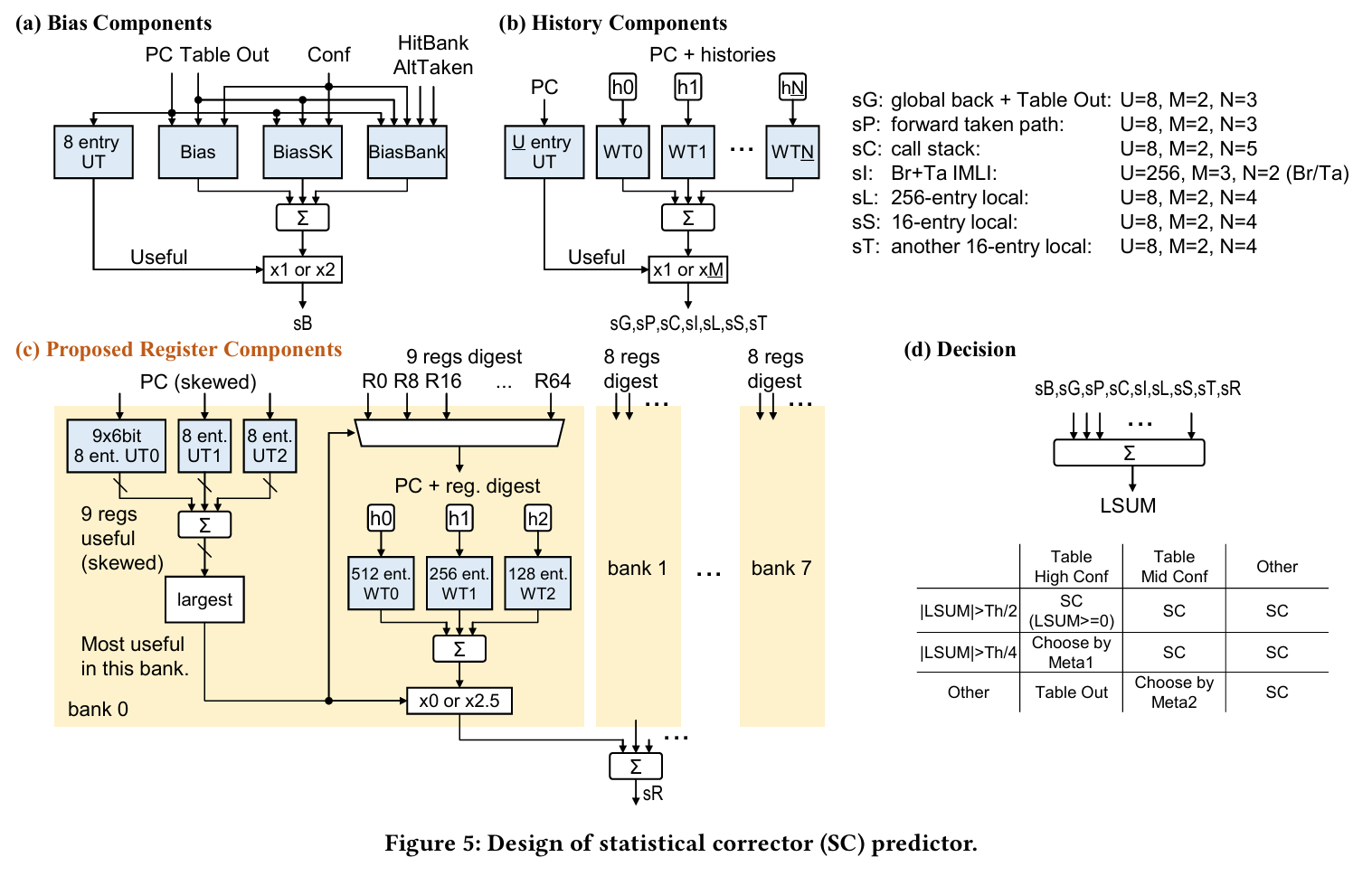
Bias Component:
sB: Bias
History Components:
sG: Global backward dir
sP: Forward taken path
sL: 1st local
sS: 2nd local
sT: 3rd local
sC: Call-stack
sI: IMLI
Register Component:
sR: Register
Usefulness weight table (UT) 记录是否可信 (tracks prediction usefulness)
Prediction weight table (WT) 记录是否跳转 (determines the predicted branch direction)
struct SimpleComponent
indexed by pc_hash, full_hist and args
get_value return (2*ctr+1)
struct WeightGroup
1
2
std::array<int8_t, 1 << LogSize> weight_ctr; // UT
std::vector<SimpleComponent> components; // WT
UT: PC-indexed; 8 ents. * 6 bits/ent.
由UT相应表项是否≥0来决定权重(x1 or x2)
Bias Component
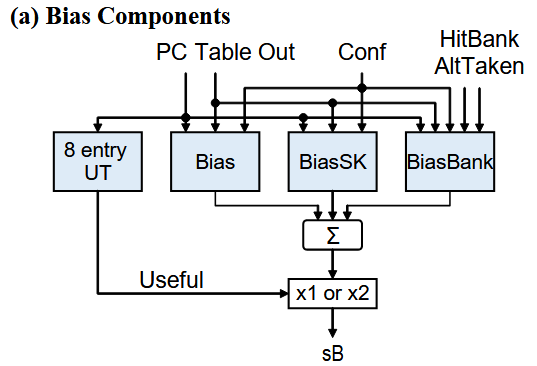
struct wBias : WeightGroup
sum after (2*ctr+1)
WT: indexed by pc_hash and args
sBiasNormal: 1K ents. * 7 bits/ent.
sBiasSkew: 1K ents. * 7 bits/ent.
sBiasBank: 1K ents. * 7 bits/ent.
x1 or x2
History Components
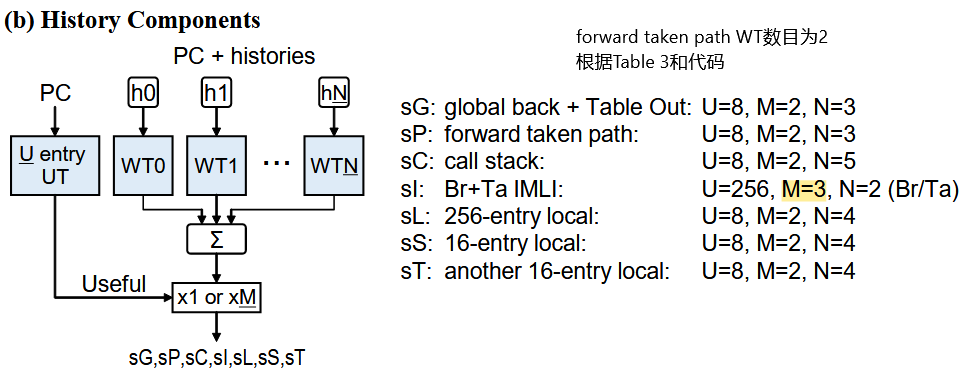
struct wGEHL : WeightGroup
sum after (2*ctr+1)
WT: indexed by pc_hash and full_hist
global_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC, pred_inter and GHIST
history lengths: 40, 24, 10
3 tables * 2K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
path_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC and fphist
history lengths: 16, 9
2 tables * 1K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
local1_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC and local1_hist(PC)
history lengths: 18, 11, 6, 3
4 tables * 2K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
local2_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC and local2_hist(PC)
history lengths: 21, 16, 11, 6
4 tables * 2K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
local3_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC and local3_hist(PC)
history lengths: 19, 14, 9, 4
4 tables * 2K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
call_stack_GEHL_components
WT:
indexed by PC and call_stack_hist
history lengths: 47, 31, 18, 10, 5
5 tables * 2K ents./table * 6 bits/ent.
IMLI_components
struct IMLI_WeightGroup
1
2
std::array<int8_t, 1 << LogSize> weight_ctr;
std::vector<SimpleComponent> components;
UT: PC-indexed; 128 ents. * 6 bits/ent.
由UT相应表项是否≥0来决定权重(x1 or x3)
WT:
sBrIMLI:
indexed by PC and BrIMLI
1K ents. * 6 bits/ent.
sTaIMLI:
indexed by PC and TaIMLI
2K ents. * 6 bits/ent.
Register Component
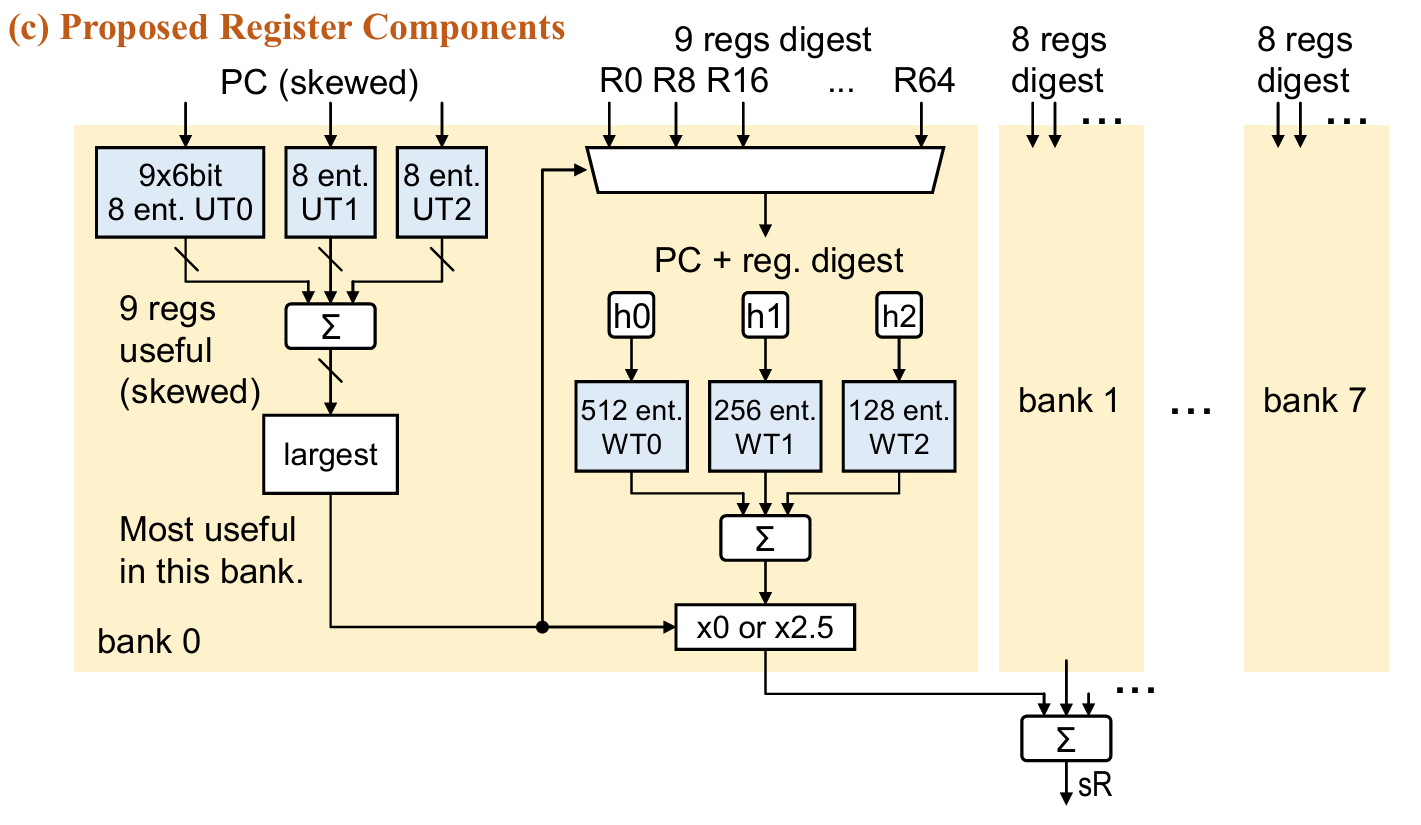
class RBias_
WT:
indexed by PC, reg. digest and reg. number
3 tables/bank * 8 banks
(512 ents. * 6 bits/ent.) + (256 ents. * 6 bits/ent.) + (128 ents. * 6 bits/ent.)
class WR_
UT:
65个寄存器,每个寄存器3张表
每张表 8 ents. * 6 bits/ent.
PC(skewed)-indexed
每个bank中对应regs.各自UT表项加和,选出最大的,按是否≥0决定x0 or x5,对most useful reg. in this bank对应的WT表项加和,乘以权重,8个bank再求和得sR。
Register Component中所有求和均为直接相加,不进行(2*ctr+1)。
RegFileState
decode_notify
execute_notify
65 ents., one for each logical reg.
RegFileStateEntry:
valid(1-bit): clear at decode and set when the instruction completes at execute (for the inst.’s dst. reg.)
payload(14-bit): write ROB index (12-bit) at decode (as a tag) and reg. digest (14-bit) when the instruction completes at execute
ctr(8-bit, unsigned): decay_ctr, serves as age. Increment when an inst. gets decoded and get reset when reach 255.
Whenever the branch predictor queries the table, any entry whose valid bit is set forwards its digest to the register-value components in the SC for prediction.
make_reg_digest
RUNLTS generates a 12-bit digest from each 64-bit register value, with the format depending on the register type.
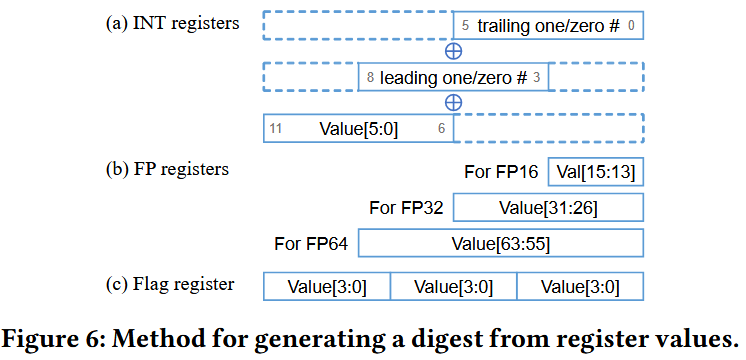
Tracking available registers: Tomasulo-like tabular method
At decode stage
Invalidate the digest of destination register
Record a tag (ROB index)
(Invalidate too old digests)
At execution stage
Record a digest if the tag matches
At prediction stage
Use only valid digests
Predict
bool predict_using_given_hist(uint64_t seq_no, uint8_t piece, UINT64 PC, cbp_hist_t& hist_to_use, const bool pred_time_predict)
/// @param pred_time_predict 是否是在预测阶段调用
TAGE:
Tagepred
SC:
Register Component中7个bank每个bank中对应regs.各自UT表项加和,选出最大的(相等的话先到先得),按是否≥0决定x0 or x5,对most useful reg. in this bank对应的WT表项加和,乘以权重,8个bank再求和得sR
Bias Component, History Components各组件各自计算
加和得LSUM,SCPRED = (LSUM ≥ 0)
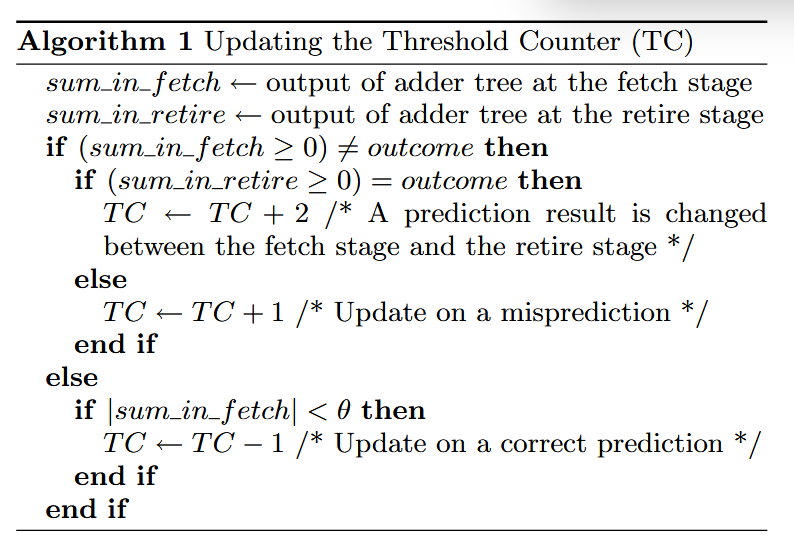
Dynamic Threshold Fitting 动态阈值调整
idea from FTL++ (Revisiting local history to improve the fused two-level branch predictor, Algorithm 1 Updating the Threshold Counter (TC))
组件
updatethreshold — 全局阈值(12-bit)
Pupdatethreshold[INDUPD] — 局部阈值数组(PC-indexed, 64 ents. * 8 bits/ent.)
SC各组件的extra_weight — 各个SC组件对当前分支预测置信度的“贡献度”或“重要性”
1
2
const int base_threshold = (updatethreshold >> 1) + Pupdatethreshold[INDUPD];
pv.THRES = base_threshold + 6 * extra_weight;
Decision
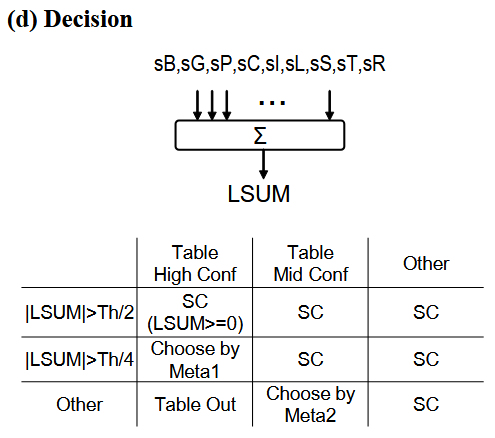
two meta predictors: FirstH, SecondH (7-bit each)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
int chooser() const
{
// Tage和SC预测相左
if (pred_inter != SCPRED) {
if (HighConf) {
if (abs(LSUM) < THRES / 4) {
return 0; // use pred_inter
} else if (abs(LSUM) < THRES / 2) {
return 2; // use SecondH<0 ? SCPRED : pred_inter
} else {
return 3; // use SCPRED
}
} else if (MedConf) {
if (abs(LSUM) < THRES / 4) {
return 1; // use FirstH<0 ? SCPRED : pred_inter
} else {
return 3; // use SCPRED
}
} else {
return 3; // use SCPRED
}
} else {
return 3; // use SCPRED (== pred_inter)
}
}
Update
SC_update
根据Tage预测是否正确 Train FirstH and SecondH (在预测时用到 FirstH or SecondH 的情况下)
Threshold Update
1
2
3
4
bool sum_at_prediction_is_weak = abs(hist_to_use.perceptron_sum_at_prediction) < pv.THRES;
bool sum_at_train_is_weak = abs(pv.LSUM) < pv.THRES;
bool mispred_at_prediction = (hist_to_use.perceptron_sum_at_prediction >= 0) != resolveDir;
bool mispred_at_train = (pv.LSUM >= 0) != resolveDir;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
if (mispred_at_prediction and not mispred_at_train) {
threshold_update(+6); // FTL++-like threshold update. There are strong perturbations 扰动.
}
if (mispred_at_prediction and mispred_at_train) {
threshold_update(+1); // Mispredictions; increase the threshold (there are many perturbations)
}
if (not mispred_at_prediction and sum_at_prediction_is_weak and sum_at_train_is_weak) {
threshold_update(-1); // A weak prediction is correct; decrease the threshold (there are small perturbations)
}
// Do not decrease the threshold in the cases wehere sum_at_prediction_is_weak but not sum_at_train_is_weak; it may be a loop begining.
SC 子组件更新
if (mispred_at_train or sum_at_train_is_weak)
Bias Component and History Components except IMLI Component
UT更新
把更新阶段预测结果(LSUM)去掉该组件的影响,分别尝试两个权重(重新参与求和),如果权重影响了预测结果(即关于是否LSUM≥0,两个预测不一致),说明这个权重是“关键因子”:如果该组件预测正确,++ctr;否则–ctr
WT更新
根据实际是否跳转,跳转则++ctr,否则–ctr
IMLI Component in History Components
UT更新
把更新阶段预测结果(LSUM)去掉该组件的影响,分别尝试两个权重(重新参与求和),如果权重影响了预测结果(即关于是否LSUM≥0,两个预测不一致),说明这个权重是“关键因子”:如果该组件预测正确,++ctr;否则–ctr
WT更新
如果 get_extra_weight(PC) 为 0 (对应权重为1),执行一次;如果为 2 (对应权重为3),执行 3 次:(有用的特征强化学习)
根据实际是否跳转,跳转则++ctr,否则–ctr
Register Component
覆盖所有bank
训练 被用到的bank(即预测阶段该bank中有reg. useful≥0)
UT更新
把更新阶段预测结果(LSUM)去掉该组件的影响,分别尝试两个权重(重新参与求和),如果权重影响了预测结果(即关于是否LSUM≥0,两个预测不一致),说明这个权重是“关键因子”:如果该组件预测正确,++ctr;否则–ctr
WT更新
(对该bank中预测阶段最终使用的reg.(即最useful的)对应的三张WT)根据实际是否跳转,跳转则++ctr,否则–ctr
训练 未被用到的bank
随机找一个起始位置,对每个未被用到的bank进行一次上述训练(即受到训练的reg.在一定程度上是随机的)
历史管理与 Checkpoint
struct cbp_hist_t
1
2
3
cbp_hist_t active_hist; // running history always updated accurately
// checkpointed history. Can be accesed using the inst-id(seq_no/piece)
std::unordered_map<uint64_t /*key*/, cbp_hist_t /*val*/> pred_time_histories;
1
2
3
uint64_t phist; // path history
std::array<uint8_t, HISTBUFFERLENGTH> ghist; // 8K-ents.(1 bit/ent.) Global History Buffer (事实上存的不是纯粹的taken/not taken)
int ptghist; // 指向当前历史位的指针(循环 buffer 用)
TAGE
Global History: 即最长表所需历史长度 m[23] = 4316 bits
Path History: 27 bits
1
2
3
4
using tage_index_t = std::array<folded_history, NHIST + 1>;
using tage_tag_t = std::array<folded_history, NHIST + 1>;
tage_index_t ch_i; // checkpoint 的索引折叠历史(每表一个)
std::array<tage_tag_t, 2> ch_t; // 两组 tag 折叠历史
SC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
uint64_t GHIST; // global backward taken history, 40 bits
uint64_t fphist; // forward taken path history, 16 bits
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal1::FeatureSize> L_shist; // PC-indexed, 256 ents. * 18 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal2::FeatureSize> S_slhist; // PC-indexed, 16 ents. * 21 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal3::FeatureSize> T_slhist; // PC-indexed, 16 ents. * 19 bits/ent.
/**
* 可以把这看作一个定长循环栈,CallStackPtr 相当于 "栈顶指针"
* 预测器用一个有限大小的循环“调用栈”模拟函数级上下文,每次分支都写入当前帧的 taken 模式,
* 而 call/ret 只控制帧指针的移动。这样,预测器就能为不同函数维护不同的“局部分支行为历史”
*/
// 8 ents. * 47 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sCallStack::FeatureSize> C_hist; // 模拟栈帧,每帧一个行为记录
size_t CallStackPtr = 0; // 指向当前“调用帧”, 3-bit
// IMLI
uint64_t last_backward_target = 0; // 64-bit
uint64_t last_backward_pc = 0; // 64-bit
uint64_t BrIMLI = 0; // 10-bit
uint64_t TaIMLI = 0; // 11-bit
History Update
void HistoryUpdate(UINT64 PC, int brtype, bool pred_taken, bool taken, UINT64 nextPC)
PC 当前分支指令地址
pred_taken 本次预测的结果(是否预测为 taken)
taken 本次实际执行的结果(是否实际 taken)
nextPC 实际跳转目标
对各组件历史部件进行更新
maxt 控制对 phist/ghist/folded_histories 的更新次数:间接跳转更新更多次(3),因为它们熵高、变化大,SC/TAGE 需要更丰富的信息捕捉模式
call_stack_hist:
对当前帧(当前函数)的分支行为记录一个新的 taken/not taken,每次遇到分支(无论什么类型),都记录一次
遇到函数调用(call),进入新栈帧,把 CallStackPtr 向前移一格
遇到函数返回(ret),退回上一个帧
IMLI:
TaIMLI 表示 目标地址维度的迭代计数器
判断当前跳转目标 nextPC 是否与上次 within the same « region »(128字节):
如果是在:意味着我们还在同一个循环中 ⇒ 递增迭代计数器
否则,跳到了一个新的循环 ⇒ 重置计数器
BrIMLI 表示 分支地址维度的迭代计数器
判断当前分支 PC 是否和上次 within the same « region »(128字节)
如果在 ⇒ 说明仍在执行同一个循环控制分支 ⇒ 递增 BrIMLI
否则,进入了另一个控制点 ⇒ 重置
更新 last_backward_target 和 last_backward_pc,用于下次检测是否进入了“同一个循环”
Overall Mechanism
Predict
get_cond_dir_prediction
This function is called by the simulator for predicting conditional branches.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
bool predict(uint64_t seq_no, uint8_t piece, UINT64 PC)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= 64; ++i) {
active_hist.register_values.at(i) = RegFileState.at(i).valid ? RegFileState.at(i).payload : -1; // hashed_value
}
pred_time_histories.emplace(get_unique_inst_id(seq_no, piece), active_hist); // checkpoint current hist
const bool pred_taken = predict_using_given_hist(seq_no, piece, PC, active_hist, true /*pred_time_predict*/);
pred_time_histories.at(get_unique_inst_id(seq_no, piece)).perceptron_sum_at_prediction = pv.LSUM;
return pred_taken;
}
Update
- 预测完会推测性更新各组件的历史部件
- 在execute阶段
- 使用推测性更新后的预测器再次预测
- 对各组件其他部件(UT、WT等)进行更新
Update at Prediction
spec_update
This function is called by the simulator for updating the history vectors and any state that needs to be updated speculatively. The function is called for all the branches (not just conditional branches). To faciliate accurate history updates, spec_update is called right after a prediction is made.
根据inst_class对br_type赋值,并调用HistoryUpdate函数
Update at Execute
notify_instr_execute_resolve
This function is called when any instructions (not just branches) gets executed.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
void update(uint64_t seq_no, uint8_t piece, UINT64 PC, bool resolveDir, bool predDir, UINT64 nextPC)
{
const auto pred_hist_key = get_unique_inst_id(seq_no, piece);
auto& pred_time_history = pred_time_histories.at(pred_hist_key);
// 因为这里调用了predict_using_given_hist,所以pv.LSUM已经是更新后的值了
const bool pred_taken = predict_using_given_hist(seq_no, piece, PC, pred_time_history, false /*pred_time_predict*/);
update(PC, resolveDir, pred_taken, nextPC, pred_time_history);
pred_time_histories.erase(pred_hist_key);
}
void update(UINT64 PC, bool resolveDir, bool pred_taken, UINT64 nextPC, const cbp_hist_t& hist_to_use)
{
#ifdef SC
SC_update(PC, resolveDir, hist_to_use);
#endif
TAGE_allocation(PC, resolveDir, pred_taken);
TAGE_train(PC, resolveDir);
} // END PREDICTOR UPDATE
复现
Everyone is welcome to reach out and exchange ideas.
Please credit the source as Frogman's Blog (https://frogmanr9.github.io) and include the link to this article (https://frogmanr9.github.io/posts/runlts-reading-notes/). Thank you.
This page has views.