基于 gem5 复现 RUNLTS 分支预测器
本文介绍如何在 gem5 模拟器上实现自己的分支预测器,并展示 CBP-6 冠军项目 RUNLTS 在 gem5 上的复现。
背景介绍
gem5 是一个模块化的、基于离散事件驱动的计算机系统模拟平台。本文使用 gem5 version 22.0.0.0 对第六届分支预测大赛(CBP-6)的冠军项目 RUNLTS 进行复现。
gem5 的相关资料可以在 官网 找到,不在此赘述。CBP-6 的官方模拟器和接口定义可见 GitHub 仓库。
RUNLTS 全称是 Register-value-aware predictor Utilizing Nested Large TableS,论文、源代码、PPT 和演讲视频可以在 CBP2025 Workshop Program 中找到。RUNLTS 基于 TAGE-SC-L 预测器,主要由 TAGE 和 SC 两大模块组成(loop 预测器实现复杂而对预测正确率贡献不大,因此不采用)。其中 SC 包含 Bias 部件、History 部件和 Register 部件,所有组件均由 Usefulness Weight Table(UT)和 Prediction Weight Table(WT)组成(二者内部表项均为有符号饱和计数器):UT 指示本组件有用程度,决定权重,根据本组件是否预测正确更新;WT 指示本组件预测方向,根据分支实际方向更新。
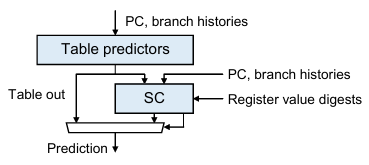
TAGE 模块采用 Allocation Throttling(来自 BATAGE),新分配表项越有用,分配就越激进。
TAGE 模块采用结合二阶等差和一阶几何的混合序列选择使用的分支历史长度。
History 部件中的 IMLI 组件采用了 André Seznec 新提出的 BrIMLI 和 TaIMLI(来自 TAGE: an engineering cookbook),分别记录跳转起始地址和目标地址与上次在同一区域(128 Bytes)内的次数,考察其与分支方向的关系。
SC 模块整体采用动态阈值调整策略(来自 FTL++),由全局阈值、局部阈值和该分支下 SC 各组件权重共同决定阈值,并根据预测阶段预测和训练阶段预测的正误与强弱来调整全局和局部阈值。
Register 部件是该项目最大的创新点,考察各逻辑寄存器的值与分支方向的关系。在 decode 阶段清除指令目的寄存器在 RegFileState 中对应表项的有效位并记录tag,execute 阶段计算完毕后将寄存器值生成的 digest 存入对应表项(要求 tag 匹配)并置有效。
RUNLTS 论文和源代码的详细解析可以参见 RUNLTS: Register-value-aware Predictor Utilizing Nested Large Tables 论文与源代码阅读笔记。
本文在 gem5 分支预测模块简介 的基础上进行,建议首先阅读该文章。
在 gem5 中实现自己的分支预测器
参考资料
操作流程
本节以 RUNLTS 为例介绍如何在 gem5 中实现自己的分支预测器,不涉及 RUNLTS 的细节。作者在复现之初对如何下手比较困惑,Enoch2090 的博客 起到了很好的指导作用,本节也主要参考这篇文章,希望对后来者有所帮助。
gem5 分支预测器的相关代码在 src/cpu/pred/ 目录下,可以参考以下预测器了解 gem5 中预测器的实现方式:
BPredUnit(bpred_unit.hh and .cc):其他预测器(直接或间接)以之为基类;BiModeBP(bi_mode.hh and .cc):直接继承自 BPredUnit,学习各个虚函数的作用;TAGE(tage.hh and .cc):进一步明确历史管理的实现方式。
这里我们直接继承 BPredUnit 复现 RUNLTS。
要想实现自己的分支预测器,主要需要做三个部分的改动。
src/cpu/pred/runlts.hh and .cc
在这里实现预测器的具体逻辑。
在 runlts.hh 中包含以下头文件:
1
2
3
#include "cpu/pred/bpred_unit.hh"
#include "debug/RUNLTS.hh"
#include "params/RUNLTS.hh"
后两个头文件由 gem5 的构建系统自动生成:
- gem5 的调试打印是通过 debug flags 控制的。gem5 的 SCons 会根据这些定义生成
build/<ISA>/debug/下的 C++ 文件(比如 debug/Branch.hh),包含宏定义。 - 在 C++ 的
build/<ISA>/params/头文件里,每个SimObject都有一个Params类,用宏或模板自动生成参数定义。每个 C++SimObject都有个SimObject.py脚本(由 SCons 自动生成),它会把 Python 的关键字参数映射到 C++ 的Params类里。Python 脚本运行时,会解析用户传入的参数,填充到对应的Params对象里,再传给 C++SimObject构造函数。
我们的 RUNLTS 类直接继承自 BPredUnit,需要重写 BPredUnit 的五大纯虚函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
void uncondBranch(ThreadID tid, Addr PC, void * &bp_history) override;
void squash(ThreadID tid, void *bp_history) override;
bool lookup(ThreadID tid, Addr branch_addr, void * &bp_history) override;
void btbUpdate(ThreadID tid, Addr branch_addr, void * &bp_history) override;
void update(ThreadID tid, Addr branch_addr, bool taken, void *bp_history,
bool squashed, const StaticInstPtr & inst, Addr corrTarget) override;
这五个函数的作用可以参见 历史维护及相关函数,不在此赘述。
src/cpu/pred/BranchPredictor.py
在这里注册一个新的 SimObject 类。
直接在该文件末尾添加:
1
2
3
4
class RUNLTS(BranchPredictor):
type = 'RUNLTS'
cxx_class = 'gem5::branch_prediction::RUNLTS'
cxx_header = "cpu/pred/RUNLTS.hh"
如果想在这里设置参数,可以参照其他预测器接着往下写。
src/cpu/pred/SConscript
在这里添加 SCons 编译脚本,向 gem5 的构建系统(SCons)注册增加的类和文件。
在 SimObject('BranchPredictor.py', sim_objects=[…]) 列表的末尾加上 'RUNLTS',并在文件中添加
1
2
Source('runlts.cc')
DebugFlag('RUNLTS')
在运行的命令中可以加上 --debug-flags=RUNLTS --debug-file=debug.txt
在上面的工作完成后,需要重新构建 gem5,然后就可以使用我们自定义的分支预测器跑程序了。
RUNLTS 的复现
有两点需要提前声明:
- 这里只进行建模,不过多考虑硬件实现;
- 复现过程中最底层的逻辑基本忠实于原作者代码,有改动会在此说明。
基本架构
TAGE
作者定义了 class RUNLTS_TAGE,在其中实现了 RUNLTS TAGE 模块的相关部件和逻辑。各分支指令的 TAGE 预测信息由 TAGE_Info 维护:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
struct TAGE_Info
{
// prediction result
uint8_t BIM = 0; // Bimodal result
bool provider = false; // result of the longest match table
// result of the second longest match table
bool altpred = false;
bool pred = false; // ultimate prediction of TAGE
// confidence of the provider
bool LowConf = false;
bool MedConf = false; // medium confidence
bool HighConf = false;
// condidence of the altpred
bool AltConf = false; // 1 for high
// bank information
uint8_t HitBank = 0; // the table id (0-23) of the provider
uint8_t AltBank = 0; // the table id (0-23) of the altpred
// indices and tags of this branch
int BIM_idx = 0; // index to Bimodal
int tagged_idx[NUM_HIST + 1]; // indices to tagged tables
uint tagged_tag[NUM_HIST + 1]; // tags to tagged tables
TAGE_Info() {
for (int i = 0; i <= NUM_HIST ; i++) {
tagged_idx[i] = 0; tagged_tag[i]=0;
}
}
}; // struct TAGE_Info
SC
作者定义了 class RUNLTS_SC,在其中实现了 RUNLTS SC 模块的相关部件和逻辑。各分支指令的 SC 预测信息由 SC_Info 维护:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
struct SC_Info
{
// TAGE out
bool TAGE_pred = false;
bool provider = false;
bool altpred = false;
bool LowConf = false; // confidence of the provider
bool HighConf = false; // confidence of the provider
uint8_t HitBank = 0; // the table id (0-23) of the provider
// SC
int THRES = 0; // note that THRES is per-branch as well
bool pred = false; // ultimate prediction of SC
int LSUM = 0; // the lastest LSUM of this branch
int perceptron_sum_at_prediction = 0; // LSUM at predition
// Register Component relevant
std::array<uint64_t, 64> register_digests = {};
int best_reg[NUM_SC_REG_BANK];
SC_Info() {
register_digests.fill(-1);
std::fill(std::begin(best_reg), std::end(best_reg), -1);
}
}; // struct SC_Info
RUNLTS
历史基本结构:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
struct RUNLTS_History
{
// Checkpoint information
tage_index_t ch_i;
std::array<tage_tag_t, 2> ch_t;
// Begin Conventional Histories
uint64_t phist; // path history
// 8K-ents.(1 bit/ent.) Global History Buffer (not pure taken/not taken)
std::array<uint8_t, HIST_BUFFER_LENGTH> ghist;
int ptghist; // ptr to the global history buffer
// For SC
uint64_t GHIST; // global backward history, 40 bits
uint64_t fphist; // forward taken path history, 16 bits
// PC-indexed, 256 ents. * 18 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal1::FeatureSize> L_shist;
// PC-indexed, 16 ents. * 21 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal2::FeatureSize> S_slhist;
// PC-indexed, 16 ents. * 19 bits/ent.
std::array<uint64_t, sLocal3::FeatureSize> T_slhist;
// 8 ents. * 47 bits/ent., simulate stack frame
std::array<uint64_t, sCallStack::FeatureSize> C_hist;
size_t CallStackPtr = 0; // point to current call frame, 3-bit
// IMLI
uint64_t last_backward_target = 0; // 64-bit
uint64_t last_backward_pc = 0; // 64-bit
uint64_t BrIMLI = 0; // 10-bit
uint64_t TaIMLI = 0; // 11-bit
uint64_t& local1_hist(Addr PC) {
return L_shist.at(sLocal1::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t& local2_hist(Addr PC) {
return S_slhist.at(sLocal2::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t& local3_hist(Addr PC) {
return T_slhist.at(sLocal3::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t& call_stack_hist() {
return C_hist.at(CallStackPtr);
}
uint64_t local1_hist(Addr PC) const {
return L_shist.at(sLocal1::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t local2_hist(Addr PC) const {
return S_slhist.at(sLocal2::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t local3_hist(Addr PC) const {
return T_slhist.at(sLocal3::get_index(PC));
}
uint64_t call_stack_hist() const {
return C_hist.at(CallStackPtr);
}
RUNLTS_History() {}
}; // struct RUNLTS_History
在具体实现中有两类历史:
- 预测器维护的历史(记作 bp_hist):在建模中作为预测器的成员;
- 各分支指令维护的历史(记作 bp_history):在建模中由分支指令携带。
作者定义了 struct RUNLTS_Info 作为各分支指令维护的信息,在 RUNLTS 类的函数中调用 RUNLTS_TAGE 类或 RUNLTS_SC 类的函数时,需要相应地将该指令的 tageInfo 或 scInfo 与其维护的 hist 一并传入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
struct RUNLTS_Info
{
RUNLTS_History hist;
bool ulti_pred = false;
bool isUncondBranch = false;
int chooser = 0; // indicate the decision to choose between TAGE and SC
TAGE_Info tageInfo;
#ifdef ENABLE_SC
SC_Info scInfo;
#endif
RUNLTS_Info() {}
}; // struct RUNLTS_Info
我们的 RUNLTS 类直接继承自 BPredUnit:class RUNLTS : public BPredUnit。在其中实现了预测器维护的历史:RUNLTS_History bp_hist,并定义了函数 update_hist,负责更新预测器维护的历史(即 bp_hist):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
void
RUNLTS::update_hist(Addr PC, bool taken,
const StaticInstPtr & inst, Addr nextPC)
{
/**
* condBranchInstClass 1
* uncondDirectBranchInstClass 0
* uncondIndirectBranchInstClass 2
* callDirectInstClass 4
* callIndirectInstClass 6
* ReturnInstClass 10
*
* note that since we have nullStaticInstPtr as default value for inst,
* every other case should test if inst is null
*/
int brtype = 0;
if (inst && inst->isCondCtrl())
brtype |= 1;
if (inst && inst->isIndirectCtrl())
brtype |= 2;
if (inst && inst->isCall())
brtype |= 4;
if (inst && inst->isReturn())
brtype |= 8;
auto& X = bp_hist.phist;
auto& Y = bp_hist.ptghist;
auto& H = bp_hist.ch_i;
auto& G = bp_hist.ch_t[0];
auto& J = bp_hist.ch_t[1];
// special treatment for indirect branchs;
int maxt = 2;
if (brtype & 1) // conditional
maxt = 2;
else if ((brtype & 2)) // uncondIndirectBranch or callIndirect or Return
maxt = 3;
if (brtype & 1) {
// backward taken only dir history (low entropy)
bp_hist.GHIST = (bp_hist.GHIST << 1)
+ (taken & (nextPC < PC));
bp_hist.local1_hist(PC) = (bp_hist.local1_hist(PC) << 1)
| taken;
bp_hist.local2_hist(PC) = ((bp_hist.local2_hist(PC) << 1)
| taken) ^ (PC & 15);
bp_hist.local3_hist(PC) = (bp_hist.local3_hist(PC) << 1)
| taken;
}
int T = ((PC ^ (PC >> 2))) ^ taken;
int PATH = PC ^ (PC >> 2) ^ (PC >> 4);
for (int t = 0; t < maxt; t++) {
bool DIR = (T & 1);
T >>= 1;
int PATHBIT = (PATH & 127);
PATH >>= 1;
// update history
Y--;
bp_hist.ghist[Y & (HIST_BUFFER_LENGTH - 1)] = DIR;
X = (X << 1) ^ PATHBIT; // phist
// updates to folded histories
for (int i = 1; i <= NUM_HIST; i++) {
H[i].update(bp_hist.ghist, Y);
G[i].update(bp_hist.ghist, Y);
J[i].update(bp_hist.ghist, Y);
}
}
X = (X & ((1ULL << PHIST_WIDTH) - 1));
// forward taken path history
if (nextPC > PC && taken)
bp_hist.fphist = (bp_hist.fphist << 3)
^ (nextPC >> 2) ^ (PC >> 1);
// for call stack history
bp_hist.call_stack_hist() <<= 1;
bp_hist.call_stack_hist() |= taken;
if (brtype & 4) { // call
bp_hist.CallStackPtr += 1;
bp_hist.CallStackPtr %= sCallStack::FeatureSize;
bp_hist.call_stack_hist() = 0;
}
if (brtype & 8) { // return
bp_hist.CallStackPtr += sCallStack::FeatureSize - 1;
bp_hist.CallStackPtr %= sCallStack::FeatureSize;
}
// IMLI from Tage cookbook
if (taken && nextPC < PC && (brtype & 2) == 0) {
// not exceeding the power of two
int prime[18] = { 1, 1, 3, 7, 13, 31, 61, 127, 251, 509,
1021, 2039, 4093, 8191, 16381, 32749, 65521, 131071 };
if (bp_hist.last_backward_target / 128
== nextPC / 128) {
bp_hist.TaIMLI = (bp_hist.TaIMLI + 1)
% prime[sTaIMLI::LogSize];
} else {
bp_hist.TaIMLI = 0;
}
if (bp_hist.last_backward_pc / 128 == PC / 128) {
bp_hist.BrIMLI = (bp_hist.BrIMLI + 1)
% (1ULL << sBrIMLI::LogSize);
} else {
bp_hist.BrIMLI = 0;
}
bp_hist.last_backward_target = nextPC;
bp_hist.last_backward_pc = PC;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
int idx = (bp_hist.ptghist + i) & (HIST_BUFFER_LENGTH - 1);
DPRINTF(RUNLTS, " ghist[%d] = %d\n", idx, bp_hist.ghist[idx]);
}
}
历史更新
原作者代码中的历史更新函数需要分支类型和目标 PC 的信息:
1
void HistoryUpdate(UINT64 PC, int brtype, bool pred_taken, bool taken, UINT64 nextPC)
在 gem5 中进行历史更新(在这里即调用 update_hist)的场景有四处:
uncondBranch函数:将本次预测记录为跳转,并据此对预测器维护的历史进行推测性更新;lookup函数:进行分支预测并记录,最后据此对预测器维护的历史进行推测性更新;btbUpdate函数:把发生 BTB miss 的分支当作 not taken 处理,并据此对推测性更新的预测器维护的历史进行修正;update函数:当发生分支预测错误,会根据这条指令的正确方向和目标地址对预测器维护的历史进行修正。
这其中,uncondBranch、lookup 的参数列表中没有分支类型和目标 PC 的信息,btbUpdate 和 update 函数也无法直接得到分支类型的信息。
对此,我们可以把推测性更新放在 uncondBranch 和 lookup 函数之外,删去这两个函数中推测性更新的内容。
在 class BPredUnit 中定义 flag 和虚函数 update_hist:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public:
void setisRUNLTS() { isRUNLTS = true; }
private:
bool isRUNLTS = false;
virtual void update_hist(Addr PC, bool taken,
const StaticInstPtr & inst = nullStaticInstPtr,
Addr nextPC = MaxAddr) {}
在 RUNLTS 的构造函数中调用 setisRUNLTS 对 isRUNLTS 置位,然后在 BPredUnit::predict 函数中将推测性更新外置,从而能够直接传入预测的目标 PC:
1
2
3
4
// RUNLTS: speculative update
if (isRUNLTS)
update_hist(pc.instAddr(), pred_taken && (!btb_miss),
inst, target->instAddr());
由于我们没有在 uncondBranch 和 lookup 函数中进行推测性更新,因此重写的 btbUpdate 函数可以什么都不做。而在上面的推测性更新中需要将 BTB miss 当作 not taken 处理。注意推测性更新须放在 set(pc, *target); 之前。
至于分支类型,我们可以在 RUNLTS::update_hist 函数中调用 inst->isCondCtrl()、inst->isIndirectCtrl() 等函数进行判断。
RUNLTS::update
在这个函数中,
- 对于无条件分支,不进行预测器各部件的更新,因为在预测时并没有使用相关部件,而是直接作为 taken;
- 对 FirstH 和 SecondH 的更新要放在 predict_at_train 之前进行,以免 predict_at_prediction 的预测结果被覆盖;
- 我们在这里非推测性地对预测器各部件进行更新:使用历史
Ri->hist而不是bp_hist,如下:1 2 3 4 5 6
TAGE.update(Ri->tageInfo, Ri->hist, tid, branch_addr, taken, Ri->ulti_pred); #ifdef ENABLE_SC SC.update(Ri->scInfo, Ri->hist, tid, branch_addr, taken, Ri->ulti_pred); #endif
Register 部件的实现
RegFileState
CBP 面向 x86 架构,RUNLTS 收集 32 个整数寄存器、32 个浮点数寄存器和 1 个 Flag 寄存器的值。
本文面向 RISC-V 架构。RISC-V 架构提供 32 个通用整数寄存器 x0 ~ x31,32 个通用浮点寄存器 f0 ~ f31,其中 x0 寄存器被设置为硬件连线的常数 0,读恒为 0,写无效。因此,我们收集 x1 ~ x31、f0 ~ f31 寄存器的值。Digest 的生成方法不变:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
uint64_t
RUNLTS_SC::make_reg_digest(uint8_t idx, uint64_t value)
{
constexpr size_t W = 12;
uint64_t hash = 0;
if (32 <= idx && idx < 64) { // FP
if (value >> 16 == 0) {
hash = value >> (16 - 3);
} else if (value >> 32 == 0) {
hash = value >> (32 - 6);
} else {
hash = value >> (64 - 9);
}
} else { // Int
// trailing_one: the number of consecutive ones from lsb
// trailing_zero
// leading_one: the number of consecutive ones from msb
// leading_zero
int leading_one = 0, leading_zero = 0;
int trailing_one = 0, trailing_zero = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
if (!((value >> i) & 1)) {
trailing_one = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
if ((value >> i) & 1) {
trailing_zero = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 63; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!((value >> i) & 1)) {
leading_one = 63 - i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 63; i >= 0; i--) {
if ((value >> i) & 1) {
leading_zero = 63 - i;
break;
}
}
hash = ((trailing_one ^ trailing_zero)) ^
((leading_one ^ leading_zero) << 3) ^ (value << 6);
}
return hash % (1 << W);
}
原作者代码中通过 decode_notify 和 execute_notify 函数在指令解码和计算完成后对 RegFileState 进行处理。在这里,我们通过 time buffer 实现各 stage 之间的通信。
在 cpu/o3/comm.hh 的 struct TimeStruct(反向通信)中增加定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
// for RISC-V RUNLTS only
// from Decode to Fetch
struct Dest_Reg_Info_Decode
{
InstSeqNum seqNum = 0;
RegId regId;
}; // struct Dest_Reg_Info_Decode
struct RUNLTS_DecodeComm
{
// <= decodeWidth && <= MaxWidth
int size = 0;
Dest_Reg_Info_Decode dst_reg_info[MaxWidth];
}; // struct RUNLTS_DecodeComm
RUNLTS_DecodeComm runltsDecode[MaxThreads];
void decodeclearPerCycle() {
for (int t = 0; t < MaxThreads; ++t) {
runltsDecode[t].size = 0;
}
}
// from IEW to Fetch
struct Dest_Reg_Info_IEW
{
InstSeqNum seqNum = 0;
RegId regId;
uint64_t value = 0;
}; // struct Dest_Reg_Info_IEW
struct RUNLTS_IEWComm
{
// <= decodeWidth && <= MaxWidth
int size = 0;
Dest_Reg_Info_IEW dst_reg_info[MaxWidth];
}; // struct RUNLTS_IEWComm
RUNLTS_IEWComm runltsIEW[MaxThreads];
void iewclearPerCycle() {
for (int t = 0; t < MaxThreads; ++t) {
runltsIEW[t].size = 0;
}
}
decode_notify
在 Decode::tick 中调用
1
toFetch->decodeclearPerCycle();
在 Decode::decodeInsts 中增加逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// for RUNLTS
auto &decode_comm = toFetch->runltsDecode[tid];
for (int i = 0; i < inst->numDestRegs(); ++i) {
RegId r = inst->destRegIdx(i);
if (!(r.is(IntRegClass) || r.is(FloatRegClass)))
continue;
if (r.is(IntRegClass) && r.index() == 0)
continue;
if (decode_comm.size >= MaxWidth)
break;
decode_comm.dst_reg_info[decode_comm.size].regId = r;
decode_comm.dst_reg_info[decode_comm.size].seqNum = inst->seqNum;
decode_comm.size++;
}
if (decode_comm.size > 0)
wroteToTimeBuffer = true;
在 class BPredUnit 中增加虚函数:
1
2
3
public:
virtual void decode_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_DecodeComm &decode_comm) {};
并在 runlts.cc 中实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
void
RUNLTS::decode_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_DecodeComm &decode_comm)
{
#ifdef ENABLE_SC
#ifndef DISABLE_SC_REG
SC.decode_notify(tid, decode_comm);
#endif
#endif
}
void
RUNLTS_SC::decode_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_DecodeComm &decode_comm)
{
int decode_num = decode_comm.size;
regfilestate_aging(decode_num);
/**
* At decode, an instruction that writes a register stores
* its ROB index as a tag in the corresponding entry
* and clears the valid bit.
*/
for (int i = decode_num - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
InstSeqNum seqNum = decode_comm.dst_reg_info[i].seqNum;
RegClassType regClass = decode_comm.dst_reg_info[i].regId.classValue();
RegIndex regIdx = decode_comm.dst_reg_info[i].regId.index();
uint8_t idx = regIdx + (regClass == FloatRegClass) * 32;
uint64_t tag = seqNum & ((1ULL << 14) - 1); // 14-bit tag
RegFileState.at(idx).ctr = 0;
if (RegFileState.at(idx).valid)
RegFileState.at(idx).valid = false;
else if (RegFileState.at(idx).payload >= tag)
continue;
RegFileState.at(idx).payload = tag;
}
}
注意:
- 使用
seqNum的低 14 位作为 tag。 - 原作者代码中的
decode_notify是每条有目的寄存器的指令调用一次,而这里是每周期解码的一组指令调用一次,因此要注意RegFileState的 aging 机制。
execute_notify
在 IEW::tick 中调用
1
toFetch->iewclearPerCycle();
在 IEW::writebackInsts 中增加逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// for RUNLTS
auto &iew_comm = toFetch->runltsIEW[tid];
RegId r = inst->destRegIdx(i);
if (iew_comm.size >= MaxWidth)
continue;
if (!(r.is(IntRegClass) || r.is(FloatRegClass)))
continue;
if (r.is(IntRegClass) && r.index() == 0)
continue;
iew_comm.dst_reg_info[iew_comm.size].regId = r;
iew_comm.dst_reg_info[iew_comm.size].seqNum = inst->seqNum;
// get reg value
PhysRegIdPtr phys = inst->renamedDestIdx(i);
RegVal bits = cpu->getReg(phys);
uint64_t value = static_cast<uint64_t>(bits);
iew_comm.dst_reg_info[iew_comm.size].value = value;
iew_comm.size++;
wroteToTimeBuffer = true;
在 class BPredUnit 中增加虚函数:
1
2
3
public:
virtual void execute_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_IEWComm &iew_comm) {};
并在 runlts.cc 中实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
void
RUNLTS::execute_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_IEWComm &iew_comm)
{
#ifdef ENABLE_SC
#ifndef DISABLE_SC_REG
SC.execute_notify(tid, iew_comm);
#endif
#endif
}
void
RUNLTS_SC::execute_notify(ThreadID tid,
const gem5::o3::TimeStruct::RUNLTS_IEWComm &iew_comm)
{
/**
* When the instruction completes, we overwrite the payload
* with the digest of the produced value and set the valid bit.
*/
for (int i = iew_comm.size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
InstSeqNum seqNum = iew_comm.dst_reg_info[i].seqNum;
RegClassType regClass = iew_comm.dst_reg_info[i].regId.classValue();
RegIndex regIdx = iew_comm.dst_reg_info[i].regId.index();
uint64_t value = iew_comm.dst_reg_info[i].value;
uint8_t idx = regIdx + (regClass == FloatRegClass) * 32;
uint64_t tag = seqNum & ((1ULL << 14) - 1); // 14-bit tag
if ((! RegFileState.at(idx).valid) &&
(RegFileState.at(idx).payload == tag)) {
RegFileState.at(idx).valid = true;
// hashed_value
RegFileState.at(idx).payload = make_reg_digest(idx, value);
}
}
}
predict
在 RUNLTS_SC::predict 中,Register 部件预测的逻辑主要分为两步:
- 在每个 bank 中选出最 useful 的 reg;
- 各 bank 选出的 best_reg(如果存在)分别查 WTs 并加和。
对于第一步,原作者代码逻辑如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
for (int i = 1; i <= 63; i++) {
if ((Si.register_digests[i] != -1) && (rUTs.get(PC, i) >= 0)) {
int current_best = Si.best_reg[i % NUM_SC_REG_BANK];
if ((current_best == -1) ||
(rUTs.get(PC, current_best) < rUTs.get(PC, i)))
Si.best_reg[i % NUM_SC_REG_BANK] = i;
}
}
可以看到,当一个 bank 中存在多于一个 reg 的 useful 值大于或等于 0 且相等时,始终是第一个(即编号最小的)reg 被选作 best_reg。
我们希望在这样的情况下实现随机选择,因此采用 Reservoir Sampling 的方法,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/**
* Modification: Reservoir Sampling
* for n equally useful regs exist in one bank
* each of them has the probability of 1/n to be chosen
*/
std::vector<int> best_val(NUM_SC_REG_BANK, -1);
std::vector<int> count(NUM_SC_REG_BANK, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= 63; i++) {
if (Si.register_digests[i] == -1)
continue;
int bank = i % NUM_SC_REG_BANK;
int cand_val = rUTs.get(PC, i);
if (cand_val < 0)
continue;
if (cand_val > best_val[bank]) {
best_val[bank] = cand_val;
Si.best_reg[bank] = i;
count[bank] = 1;
} else if (cand_val == best_val[bank]) {
// equal -> reservoir sampling
count[bank]++;
if ((parent->MYRANDOM(hist_to_use) % count[bank]) == 0) {
Si.best_reg[bank] = i;
}
}
}
其中 MYRANDOM 函数逻辑类似于原作者代码中同名函数,利用历史生成一个 32 位伪随机数。该函数作为 RUNLTS 类的成员函数,在 RUNLTS_TAGE TAGE 和 RUNLTS_SC SC 中通过 parent 指针访问。
初步性能评估
Benchmark
Benchmark 选用 Extremely Simple Microbenchmarks,有关其中各 benchmark 的描述可见 Microbench。
首先
1
2
git clone https://github.com/VerticalResearchGroup/microbench.git
cd microbench
我们使用 python3,需要将 lfsr-taps.py 中的
1
print "%5d"%count + " " + "%11d"%int(math.pow(2,count)) + " " + format(val, '#10X')+ " " + str(i)
改成
1
print("%5d" % count + " " + "%11d" % int(math.pow(2,count)) + " " + format(val, '#10X') + " " + str(i))
由于我们面向 RISC-V 指令集,需要使用 RISC-V 工具链编译,因此在 git clone 之后要对 make.rules、make.config 进行一些修改,并在 common.h 中增加 RISCV 分支。
最后
1
2
make clean
make
即可编译成功。
评估指标
我们采用 预测器性能评估和相关统计信息 中介绍的三个指标(IPC、Accuracy、MPKI)对预测器的性能进行初步评估。
复现的 RUNLTS 性能情况
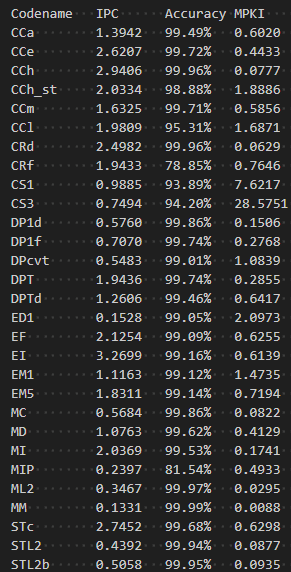
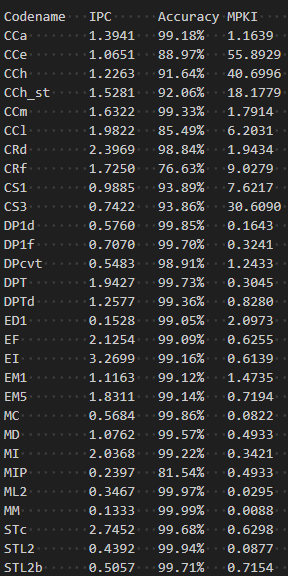
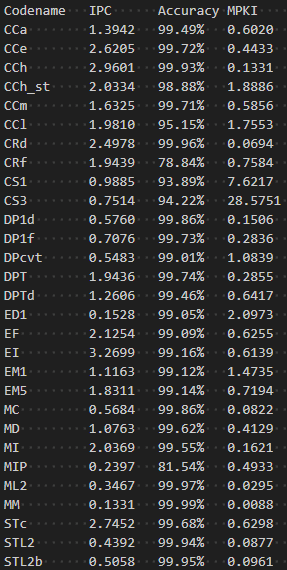
作者编写了脚本,跑完了 Microbench 中各 Benchmark,通过可配置化简单考察了一些组件的贡献,并与 gem5 自带的 TAGE_SC_L_64KB 进行简单的比较,如下:
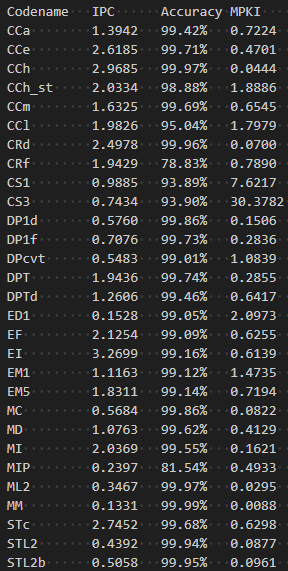
P.s.
command line:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
build/RISCV/gem5.opt \
--debug-flags=RUNLTS --debug-file=debug.txt \
configs/example/se.py \
-n 1 --cpu-type=RiscvO3CPU \
--bp-type=RUNLTS \
--caches --l2cache \
--l1i_size=64kB --l1i_assoc=4 --l1d_size=64kB --l1d_assoc=4 \
--l2_size=1MB --l2_assoc=8 \
--mem-type=DDR3_1600_8x8 --mem-size=8GB \
--cmd /home/data/frogman/microbench/CCh/bench \
--warmup-insts-no-switch 1000000 --maxinsts 1000000000
性能提升思路
- 现在的 SC 模块中的部分组件需要 TAGE 模块的结果,导致二者在预测过程中是串行工作的。可以尝试将串行改成并行,最简单的思路是将 Bias 部件等需要 TAGE 模块结果的部分去掉进行评估。
- predict_at_train 使得对预测器相关部件的访问直接 double。可以考虑限制其使用场景,例如只有在 predict_at_prediction 预测错误时进行。但这又涉及到对原本 SC 更新逻辑的较大改动。
execute_notify对于 valid 的表项放弃覆写,可能导致表项更新不够及时。THRES在 predict_at_train 以后已经改变了,但仍用于sum_at_prediction_is_weak的判断,是否恰当。
总之,还需要更加细致地分析各组件的作用、对预测准确率的贡献、对整体性能的影响,并相应地进行改进。
Everyone is welcome to reach out and exchange ideas.
Please credit the source as Frogman's Blog (https://frogmanr9.github.io) and include the link to this article (https://frogmanr9.github.io/posts/gem5-bpu-runlts/). Thank you.
This page has views.